4.1 Map集合
4.1.5 Entry键值对对象
我们已经知道,Map中存放的是两种对象,一种称为key(键),一种称为value(值),它们在在Map中是一一对应关系,这一对对象又称做Map中的一个Entry(项)。
Entry将键值对的对应关系封装成了对象。即键值对对象,这样我们在遍历Map集合时,就可以从每一个键值对(Entry)对象中获取对应的键与对应的值。
既然Entry表示了一对键和值,那么也同样提供了获取对应键和对应值得方法:
public K getKey():获取Entry对象中的键。public V getValue():获取Entry对象中的值。
在Map集合中也提供了获取所有Entry对象的方法:
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象的集合(Set集合)。
4.1.6 Map集合遍历键值对方式
键值对方式:即通过集合中每个键值对(Entry)对象,获取键值对(Entry)对象中的键与值。
操作步骤与图解:
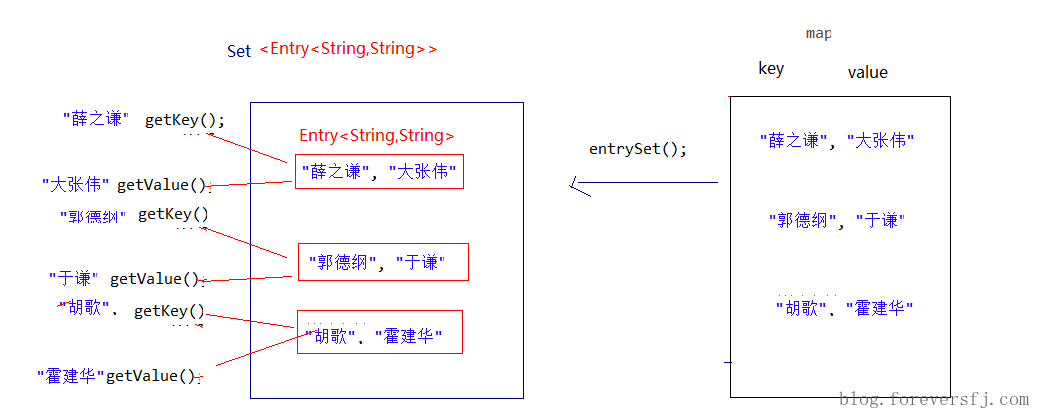
获取Map集合中,所有的键值对(Entry)对象,以Set集合形式返回。方法提示:entrySet()。
遍历包含键值对(Entry)对象的Set集合,得到每一个键值对(Entry)对象。
通过键值对(Entry)对象,获取Entry对象中的键与值。 方法提示:getkey() 、getValue()。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class MapDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("胡歌", "霍建华");
map.put("郭德纲", "于谦");
map.put("薛之谦", "大张伟");
Set<Entry<String,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, String> entry : entrySet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"的CP是:"+value);
}
}
}
|
遍历图解:
Tips:
Map集合不能直接使用迭代器或者foreach进行遍历。但是转成Set之后就可以使用了。
4.1.7 HashMap存储自定义类型键值
练习:每位学生(姓名,年龄)都有自己的家庭住址。那么,既然有对应关系,则将学生对象和家庭住址存储到map集合中。学生作为键, 家庭住址作为值。
注意,学生姓名相同并且年龄相同视为同一名学生。
编写学生类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o)
return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass())
return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
|
编写测试类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Student,String>map = new HashMap<Student,String>();
map.put(newStudent("lisi",28), "上海");
map.put(newStudent("wangwu",22), "北京");
map.put(newStudent("zhaoliu",24), "成都");
map.put(newStudent("zhouqi",25), "广州");
map.put(newStudent("wangwu",22), "南京");
Set<Student>keySet = map.keySet();
for(Student key: keySet){
Stringvalue = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key.toString()+"....."+value);
}
}
}
|
- 当给
HashMap中存放自定义对象时,如果自定义对象作为key存在,这时要保证对象唯一,必须复写对象的hashCode和equals方法。
- 如果要保证map中存放的key和取出的顺序一致,可以使用
java.util.LinkedHashMap 集合来存放。
4.1.8 LinkedHashMap
HashMap保证成对元素唯一,并且查询速度很快,可是成对元素存放进去是没有顺序的。但是,如果要保证有序,还要速度快,怎么办呢?
在HashMap下面有一个子类LinkedHashMap,它是链表和哈希表组合的一个数据存储结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class LinkedHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
map.put("邓超", "孙俪");
map.put("李晨", "范冰冰");
map.put("刘德华", "朱丽倩");
Set<Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, String> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
|
结果:
4.1.9 Map集合练习
需求:
分析:
- 获取一个字符串对象
- 创建一个Map集合,键代表字符,值代表次数。
- 遍历字符串得到每个字符。
- 判断Map中是否有该键。
- 如果没有,第一次出现,存储次数为1;如果有,则说明已经出现过,获取到对应的值进行++,再次存储。
- 打印最终结果
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请录入一个字符串:");
String line = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
findChar(line);
}
private static void findChar(String line) {
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < line.length(); i++) {
char c = line.charAt(i);
if (!map.containsKey(c)) {
map.put(c, 1);
} else {
Integer count = map.get(c);
map.put(c, ++count);
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
|
本文标题:第三部分 第四章 1.Map集合(二)
文章作者:foreverSFJ
发布时间:2019-08-20 16:58:11
最后更新:2019-08-20 16:58:11
原始链接:Notes/Java/Basic/Part03/04_1_2 Map集合(二).html
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明出处!

